
- #Difference between tabular reports and matrix reports how to
- #Difference between tabular reports and matrix reports pro
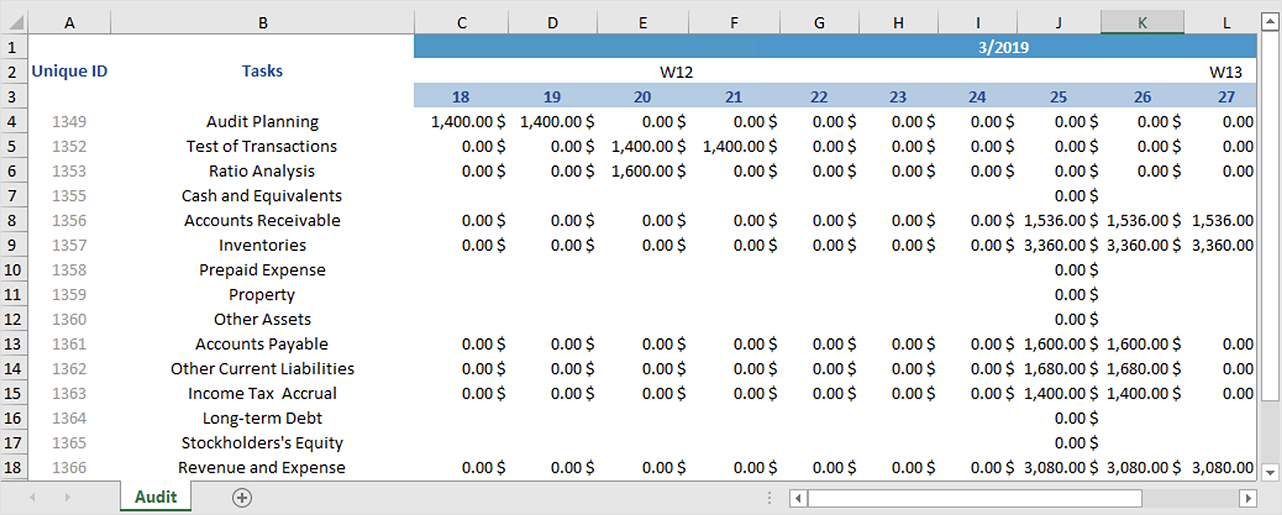
In the Visualizations pane, when you add multiple fields to the Rows section of the Fields well, you enable drill-down actions on the rows of the matrix visual. Let's take a look at how each of these works. This includes the ability to drill down using rows, columns, and even into individual sections and cells. With the matrix visual, you can do all sorts of interesting drill-down activities that weren't available before. Using drill-down actions with the matrix visual For more information, see Work with multidimensional models in Power BI. If you're building a report on top of an Analysis Services multidimensional model, there are some special considerations for expand/collapse if the model uses the Default Member feature. When that dashboard tile is selected, and the report opens, the expansion state can still be changed in the report. A matrix can be pinned to a dashboard expanded or collapsed. The expansion state of the matrix will save with your report. Once the icons are turned on, they work similar to PivotTable icons in Excel. By default, the icons will match the formatting of the row header, but you can customize the icons’ colors and sizes separately if you want. You can also add +/- buttons to the row headers through the formatting pane under the Row headers card. You have similar options for collapsing row headers as well. You’ll see options to expand the specific row header you selected, the entire level, or everything down to the very last level of the hierarchy. The first is through the right-click menu. There are two ways you can expand row headers. They aren't solely based on the visible values. When you look at totals and subtotals, remember that those values are based on the underlying data. This is a common pattern when the value you’re summing is on the ‘one’ side of a one-to-many relationship. Thus, the accurate total from the underlying data, and a simple addition of the visible values, do not equate. However, since a salesperson shows up against multiple dates, the numbers can appear more than once. In this example, each row in the matrix visual farthest to the right is showing the Amount for each salesperson/date combination. Take a look at the following matrix visuals. This means you can end up with different values in the total row than you might expect. For total and subtotal rows, Power BI evaluates the measure over all rows in the underlying data – it isn't just a simple addition of the values in the visible or displayed rows.
#Difference between tabular reports and matrix reports how to
Understanding how Power BI calculates totalsīefore jumping into how to use the matrix visual, it's important to learn how Power BI calculates total and subtotal values in tables and matrices.
#Difference between tabular reports and matrix reports pro
On the Axis Options tab, check the Align axes in box, and then in the dropdown box, select the group on which to align the axis.Sharing your report with a Power BI colleague requires that you both have individual Power BI Pro licenses or that the report is saved in Premium capacity. Align the data in a sparkline or data barĪdd a sparkline or data bar to a table or matrix.Ĭlick in the sparkline or data bar, and then click Horizontal Axis Properties or Vertical Axis Properties.
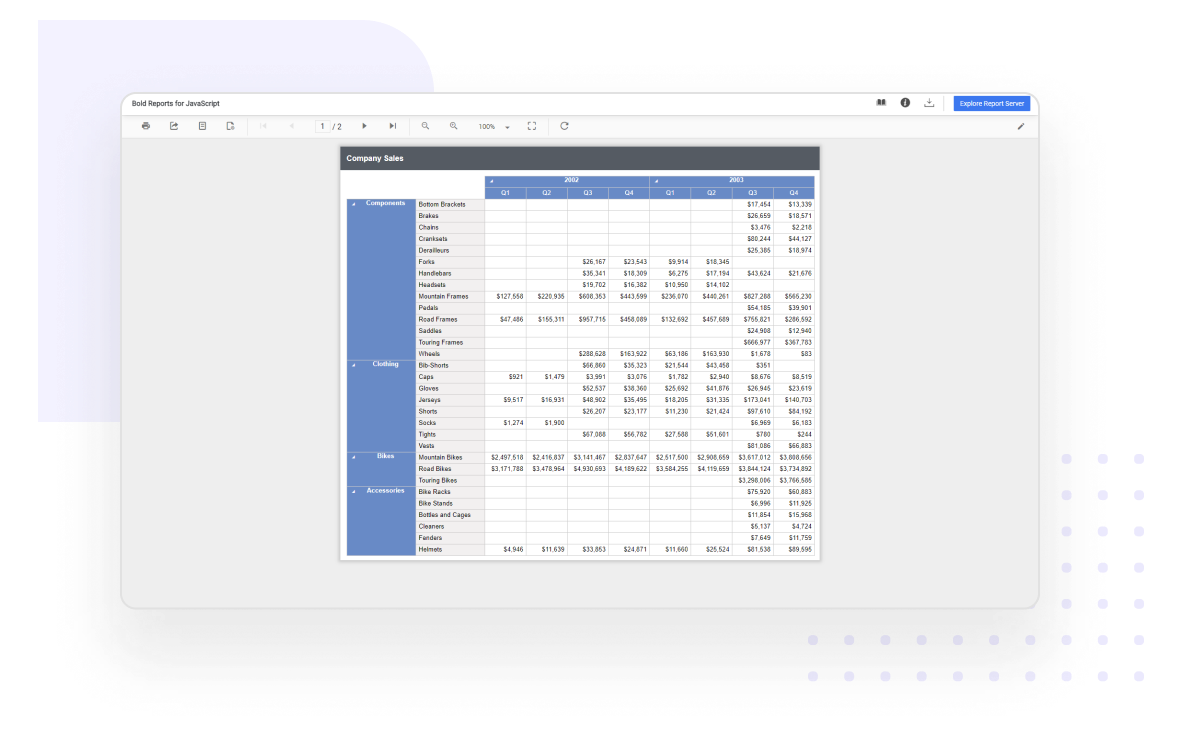
For more information, see Sparklines and Data Bars (Report Builder and SSRS). It also aligns the charts vertically by making the sizes of the different charts relative to each other. Note that for days that an employee has no sales, the chart leaves a blank and aligns subsequent days horizontally. In this image, the column chart shows daily sales for each employee. In a paginated report, when you check this option the values in your sparklines and data bars will align across the different cells in the table or matrix, even if there are missing values in the data they are based on. Sparklines and data bars are small, simple charts that convey a lot of information with little extraneous detail in a paginated report. Align the data in a paginated report chart in a table or matrix (Report Builder)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
